By charnwit kheanpanya
29/4/2014,21.45
The 1st law of thermodynamics is a version of the law of conservation of energy that internal energy change of a system equals net heat transfer minus net work done by the system. where heat and work are the methods of transferring energy for a system in thermal equilibrium. Q represents the net heat transfer—it is the sum of all heat transfers into and out of the system. Q is positive for net heat transfer into the system. W is the total work done on and by the system. W is positive when more work is done by the system than on it. The change in the internal energy of the system, ΔU, is related to heat and work by the first law of thermodynamics, ΔU=Q−W.
 |
| internal energy |
The relationship between internal energy and work can be understood by
considering another concrete example: the tungsten filament inside a light bulb. When work
is done on this system by driving an electric current through the tungsten wire, the
system becomes hotter and 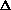 E is therefore positive. (Eventually, the wire becomes hot enough
to glow.) Conversely,
E is therefore positive. (Eventually, the wire becomes hot enough
to glow.) Conversely, 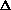 E
is negative when the system does work on its surroundings.
E
is negative when the system does work on its surroundings.
The sign conventions for heat, work, and internal energy are summarized in
the figure below. The internal energy and temperature of a system decrease (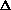 E < 0) when the system
either loses heat or does work on its surroundings. Conversely, the internal energy and
temperature increase (
E < 0) when the system
either loses heat or does work on its surroundings. Conversely, the internal energy and
temperature increase (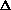 E
> 0) when the system gains heat from its surroundings or when the surroundings do work
on the system.
E
> 0) when the system gains heat from its surroundings or when the surroundings do work
on the system.








